Have you ever wondered why some male singers can hit those low, rumbling notes while others effortlessly reach high pitches?
In this blog post, we’ll closely examine the science behind the average male vocal range.
By exploring the anatomy of the male vocal tract, the role of hormones, and the impact of vocal training, we’ll uncover the factors that determine a man’s vocal range.
We’ll also examine the different voice types, such as bass, baritone, and tenor, and how they relate to the average male vocal range.
Understanding Vocal Range
Vocal range refers to the span of notes an individual can comfortably sing, from the lowest to the highest pitch. This range is typically measured in octaves, with most people having a range of around 1.5 to 2 octaves.
Understanding one’s vocal range is crucial for singers, as it helps them identify their voice type and select songs and keys that suit their capabilities.
Anatomy of Vocal Cords
The vocal cords, or vocal folds, are two bands of muscle tissue in the larynx (voice box) at the top of the trachea (windpipe). These folds play a vital role in producing sound.
When we breathe, the vocal cords remain open, allowing air to flow freely into and out of the lungs. However, when we speak or sing, the vocal cords come together and vibrate as air from the lungs passes through them.
The speed at which the vocal cords vibrate determines the pitch of the sound produced.
Singers can control the pitch of their voice by tightening or relaxing the vocal cords. Tighter vocal cords produce higher-pitched sounds, while more relaxed vocal cords create lower-pitched tones.
The vocal cords’ length and thickness influence the voice’s pitch and quality.
Average Male Vocal Range

The average male vocal range typically spans from F2 to E4.
The lowest note, F2, is usually found in deeper, more resonant male voices, while E4, the highest note, is more common in higher-pitched male voices. However, it’s important to note that individuals can vary significantly.
Some men may be able to sing lower or higher than this average range. These differences can be attributed to various factors, including unique physical characteristics and the level of vocal training an individual has received.
Factors Influencing Male Vocal Range

1. Biological Factors
One of the primary factors influencing a male’s vocal range is the anatomy of their vocal cords. The size and shape of the vocal cords play a crucial role in determining the pitch of the voice.
Larger vocal cords generally produce lower pitches, while thicker vocal cords can create richer, deeper sounds.
In addition to the vocal cords, the vocal tract’s structure also impacts the sound’s range and quality. The vocal tract’s length and shape, including the throat, nose, and mouth, can affect how the voice resonates and projects.
2. Training and Technique
Proper vocal training is essential for singers looking to extend their vocal range. Regular practice focusing on breath control, resonance, and targeted vocal exercises can help improve vocal flexibility and strength.
Seeking guidance from a professional vocal coach can provide singers with personalized training tailored to their specific needs and goals.
A skilled coach can help singers safely and effectively expand their range while minimizing the risk of strain or injury.
3. Genetics
Genetic predispositions also significantly influence an individual’s vocal range. Some people are born with longer or more flexible vocal cords, allowing for a broader range of pitches.
Additionally, vocal traits can be inherited, meaning family members may share similar vocal ranges.
While genetics are not the sole determining factor, they can contribute to an individual’s voice’s unique qualities and capabilities.
4. Age
As individuals age, their vocal cords naturally undergo changes that can affect their vocal range. The vocal cords may become less flexible, and the muscles surrounding them may weaken, leading to a potential decrease in range.
However, with regular training and proper care, singers can maintain and even improve their vocal range well into their later years.
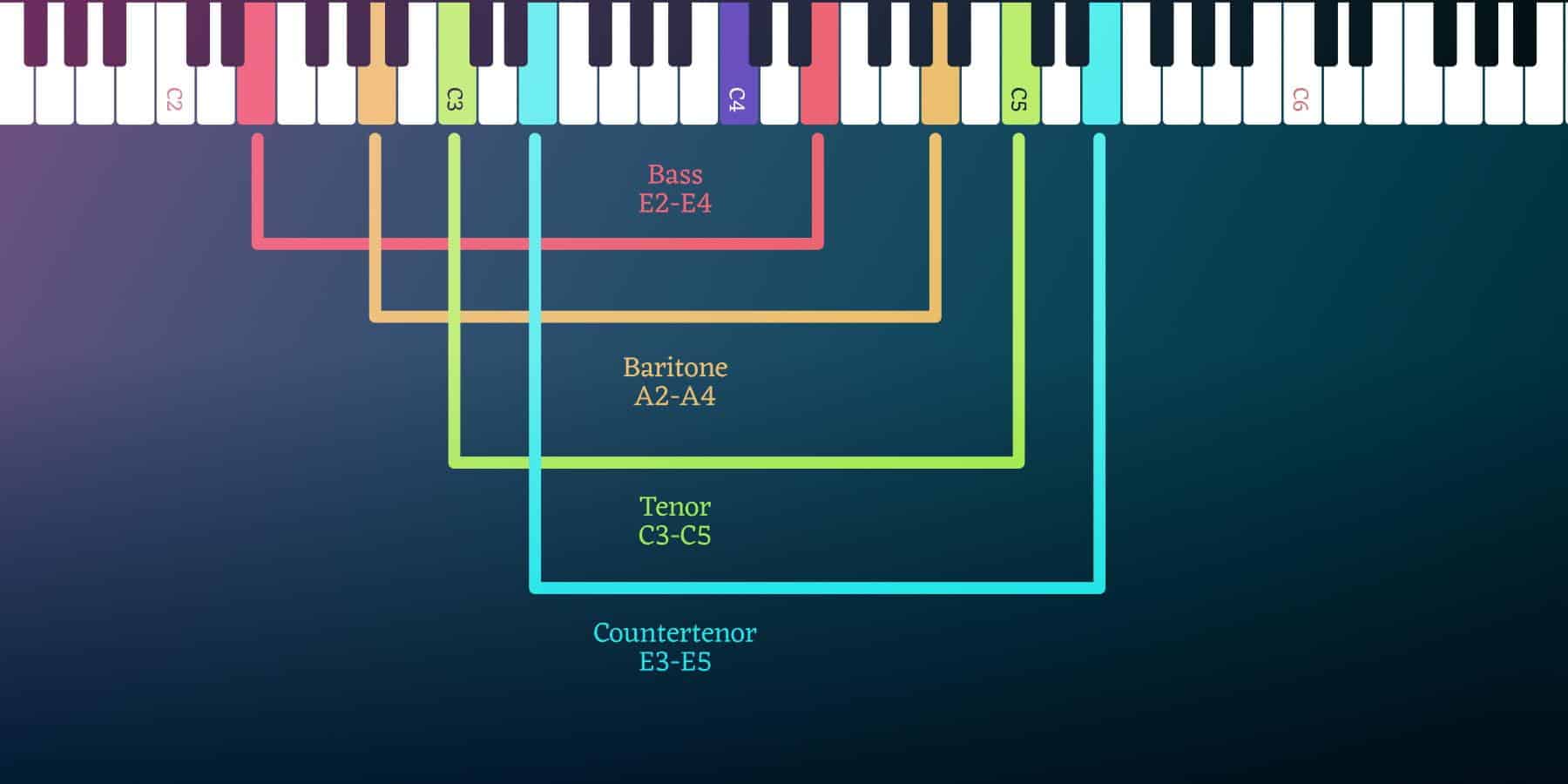
Types of Male Vocal Ranges
| Type | Range | Characteristics | Famous Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bass | C2 – E4 | Lowest male vocal range, deep and rich tones. | Johnny Cash, Barry White |
| Baritone | F2 – G4 | Mid-range male voice, versatile and full-bodied sound. | Elvis Presley, David Bowie |
| Tenor | B2 – C5 | High male voice, strong and bright tones. | Freddie Mercury, Paul McCartney |
| Countertenor | G3 – F5 | The highest male voice, similar to the female contralto, is clear and bright. | Jeff Chang, Lead singer of Soda Green |
Exercises to Expand Vocal Range
1. Warm-Up Exercises
Warming up your voice is crucial before any singing session, as it helps prevent vocal strain and injury. By gently loosening up the vocal cords, warm-up exercises prepare your voice for singing, allowing for better control and clarity.
Some effective warm-up exercises include:
- Lip Trills: Gently blow air through your lips while making a buzzing sound. This helps relax the vocal cords and improves breath control.
- Sirens: Glide smoothly from your lowest comfortable note to your highest and back down, imitating the sound of a siren. This exercise helps stretch your vocal range and improves flexibility.
- Humming: Begin with gentle hums at a comfortable pitch and gradually move up and down the scale. This warms up your entire vocal range and promotes proper resonance.
2. Range Expansion Techniques
Upper Range
To develop your upper range, focus on exercises that target your head voice or falsetto. These exercises help you gain better control and clarity in the higher parts of your range.
- Falsetto Slides: Start with a comfortable middle note and slide into your falsetto, then back down. Focus on achieving smooth transitions between your chest voice and falsetto.
- “Me, May, Ma, Mo, Mu” Exercise: Sing these vowel sounds, starting in your chest voice and moving up to your head voice. Aim for clear, resonant tones throughout the exercise.
- Octave Jumps: Begin by singing a note in your chest voice, then jump an octave higher into your head voice. This exercise helps build control and bridge the gap between your lower and upper range.
Lower Range
Concentrate on exercises that target your chest voice and vocal fry to strengthen your lower range. These exercises will help you develop a richer, more powerful sound in the lower parts of your range.
- Vocal Fry Exercise: Start by producing a relaxed, creaky sound at the very bottom of your range. This exercise helps build strength and control in your lowest notes.
- Descending Scales: Begin at a comfortable high note and sing down the scale, maintaining a full, resonant sound as you descend to lower notes.
- Humming Downward: Start with a hum at a comfortable pitch and gradually slide down to the lowest note you can reach without straining. This exercise improves control and helps you access your lower range more easily.
Practical Tips and Advice
When working on expanding your vocal range, consistency is key.
Regular practice will help you see progress and maintain the gains you make. Consider working with a qualified vocal coach who can guide you through the process, ensuring you use proper technique and avoid unnecessary strain.
Always listen to your body and notice any signs of discomfort or strain. If you experience pain or fatigue, stop singing and rest your voice. Pushing yourself too hard can lead to vocal damage.
Maintaining Male Vocal Health

1. Hydration and Rest
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining vocal health. When the vocal cords are well-lubricated, they are less likely to become dry and irritated. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before and after singing sessions.
Carry a water bottle and take frequent sips to keep your throat moist.
In addition to hydration, regular rest is essential for your voice. Vocal rest allows your vocal cords to recover and prevents fatigue. Avoid overusing your voice, and take breaks when needed.
Getting adequate sleep is also crucial, as overall body rest aids in vocal recovery.
2. Avoiding Strain
Proper singing techniques are important to prevent vocal strain and overuse. These include maintaining good posture, using proper breath support, and avoiding tension in the neck and jaw.
Be mindful of your volume control, and avoid yelling or speaking loudly for extended periods.
Always listen to your voice and notice any signs of discomfort or strain. Stop singing immediately and rest your voice if you feel any pain or fatigue. Pushing through the discomfort can lead to more serious vocal issues.
Incorporating warm-up exercises before singing and cool-down exercises afterward can help prevent strain and injury.
These exercises help prepare your vocal cords for singing and allow them to recover afterward.
3. Regular Check-Ups
Regularly consulting with a vocal coach or professional can help you maintain proper technique and address any issues that may arise.
A qualified vocal coach can provide guidance and feedback, helping you identify and correct bad habits that may harm your vocal health.
In addition to vocal training, regular check-ups with an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist can help detect and treat any vocal issues early on. These professionals can assess your vocal health and provide personalized advice on maintaining your voice.
Summing It Up
To sum up, the average male vocal range is a fascinating subject influenced by various factors, from the size of the vocal cords to the impact of training and genetics.
Understanding these elements and applying practical tips, such as proper warm-up exercises and techniques for expanding your range, can help you work towards achieving your full vocal potential.
Remember, taking care of your voice through hydration, rest, and avoiding strain is as important as regular practice.
So, whether you’re a professional singer or enjoy singing in the shower, embrace your unique voice and keep exploring its possibilities.
With dedication and the right approach, you might surprise yourself with the incredible range and power your voice can achieve.
Why not start your journey today by trying out some exercises we’ve covered?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Most Common Male Voice Type?
The most common male voice type is tenor.
Is F5 a High Note for A Male?
F5 is considered a very high note for most male singers.
What Note Do Most Men Speak in?
Most men speak around the C3 to C4 range.
What Was Freddie Mercury’s Vocal Range?
Freddie Mercury’s vocal range spanned an impressive F2 to F6.